They banded together, forming local and statewide associations to boost their reputation and up the ante on care standards. These groups became powerhouses for community building, influencing training schools, and even stepping into the political arena to advocate for legislative changes.
By 1906, things got real. The Minnesota State Graduate Nurses’ Association took a bold step and brought a lawyer on board to craft a state registration bill. They weren’t looking to keep people out of nursing. Instead, they wanted to set the bar on who could proudly wear the “registered nurse” (RN) title. This plan included a State Examiners Board to keep an eye on standards and ensure RNs were up to snuff. This move wasn’t just about elevating nurses’ status; it was about giving patients peace of mind, knowing their RN was more than capable. And from January 1, 1910, only those with the board’s seal of approval in their training could register as nurses.
Fast forward a bit, and the bill’s a hit, signed into law by Governor John A. Johnson. He even picked the State Examiners Board members from a list the nurses’ association handed him. What started with nine nurses and a dream of better standards turned into a full-blown movement, setting the stage for statewide uniformity in nursing.
Jump to today, and the Minnesota Board of Nursing is a powerhouse with 16 governor-appointed members. Among them are eight registered nurses, each bringing a solid five years of fresh experience from various corners of the nursing world – from hospital floors to the head of the class in nursing programs. We’re talking about a lineup that includes experts in everything from nurse anesthesia to midwifery and beyond. And it’s not just RNs; there are also four licensed practical nurses and four folks from outside the nursing field to keep things balanced.
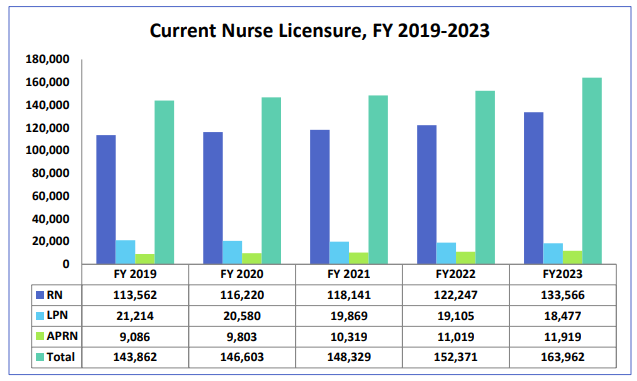
As of June 2023, Minnesota boasted 163,962 active nursing licenses. The average age of RNs active in the field was 45, LPNs a tad older at 47.5, and APRNs averaging 46.3 years, showing a broad spectrum of wisdom and expertise powering nursing in Minnesota.
Board of Nursing Minnesota Contacts
| Minnesota Board of Nursing Email | [email protected] |
| Minnesota Board of Nursing Phone Number | 612-317-3000 |
| Minnesota Board of Nursing Address | 1210 Northland Drive Suite 120Mendota Heights, MN 55120 |
| Minnesota Board of Nursing Portal | https://mn.gov/boards/nursing/ |
Minnesota State Board of Nursing Laws, Rules & Regulations
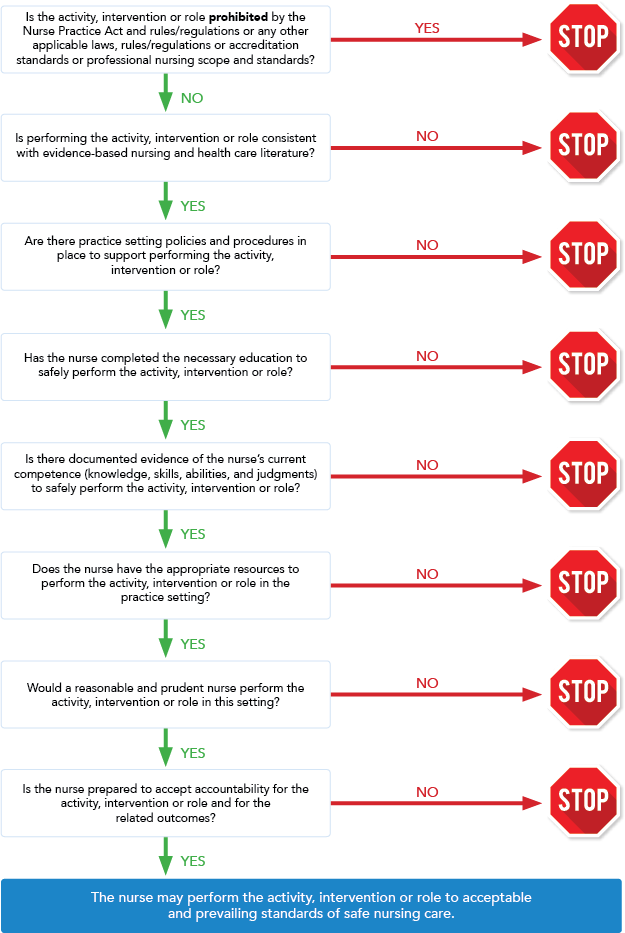
A significant decision was taken during a meeting of the Minnesota Board of Nursing in the fall of 2016. The board overwhelmingly supported the Scope of Nursing Practice Decision-Making Framework. This was a groundbreaking tool designed to demystify for nurses and the public alike which actions, interventions, or roles are squarely in line with a nurse’s education, licensure, and proven abilities, all under the umbrella of the Minnesota Nurse Practice Act.
The Board is bullish on the utility of this framework, seeing it as a beacon for nursing practice. This framework serves as a compass, aiming to elevate nursing practice by offering clear rules on professional limits.
State of Minnesota Nursing Board LPN Scope of Practice
In Minnesota, LPNs are essential, doing a variety of activities such as completing initial health assessments, notifying RNs or licensed healthcare practitioners of any changes, and helping to formulate care plans. Their responsibilities include executing nursing interventions under the supervision of an RN and distributing assignments within their team.
LPNs are also advocates for patient welfare, involved in assessing the effectiveness of interventions, collaborating with the healthcare team, educating patients, influencing policy, and maintaining care quality within their educational and experiential scope. They are taught to identify their own limitations while adhering to the norms of an authorized practical nursing education program.
Minnesota Nursing Board RN Scope of Practice
RNs in Minnesota carry out comprehensive health assessments and collaborate on crafting integrated care plans. They lead in developing and applying nursing interventions, performing critical independent actions, and efficiently delegating tasks.
Their tasks include delivering safe, effective treatment, creating a healing atmosphere, advocating for patients, and monitoring the effectiveness of initiatives. RNs are central to coordinating cross-setting care, health promotion, disease prevention, patient education, policy formulation, nursing education, and practice evaluation. Their practice is based on a strong dedication to excellent care, which is shown in their academic background and professional experience.
Minnesota Board of Nursing APRN Scope of Practice
Minnesota’s APRNs are registered and qualified by nationally recognized organizations as Clinical Nurse Specialists, qualified Nurse Practitioners, Certified Nurse Midwives, and Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists, respectively. These roles target specific patient populations, ensuring APRNs deliver top-tier care.
Their extended practice scope now encompasses sophisticated evaluation, diagnosis, medication, and therapeutic treatment, establishing them as specialists in primary care, patient care, case management, consulting, teaching, and research. With the ability to write prescriptions and administer a wide range of drugs and therapy devices, APRNs represent the pinnacle of nursing skill and patient care in Minnesota.
Minnesota Board Nursing Licensing & Certification Eligibility Requirements
The Minnesota Board of Nursing’s licensure and certification process demonstrates a careful dedication to maintaining high standards in the nursing profession.
Licensure by Examination
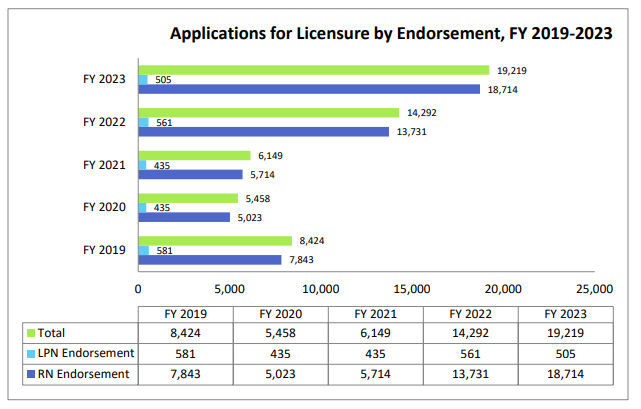
In fiscal year 2023, 5,416 licensure applications were processed, demonstrating prospective nurses’ strong enthusiasm and devotion. Candidates have to submit an application to the board, pay the appropriate fee, and realize that it is nonrefundable. Applicants undergoing reexamination are liable to higher fees, emphasizing the significance of meticulous preparation.
Eligibility criteria for licensure by examination are stringent, ensuring only the most qualified individuals proceed. Candidates must demonstrate an untarnished professional conduct history, completion of an accredited nursing program relevant to their desired licensure, and success on a national licensure examination. This exam, comprehensive in nature, may encompass various formats, including traditional, computer-based, and practical components, depending on the board’s requirements.
International applicants must also complete extra requirements, such as verifying their education to U.S. standards and, if required, demonstrating English language ability, to ensure they are fully equipped to meet the demands of the Minnesota nursing profession.
Licensure by endorsement
Recognizing the fluidity of modern nursing professions, the board supports licensure by endorsing nurses who are licensed in different states, territories, or nations. This procedure determines if an applicant’s qualifications meet Minnesota’s criteria, allowing qualified nurses to effortlessly transfer into the state’s healthcare system without re-examination.
Advanced practice registered nurse licensure
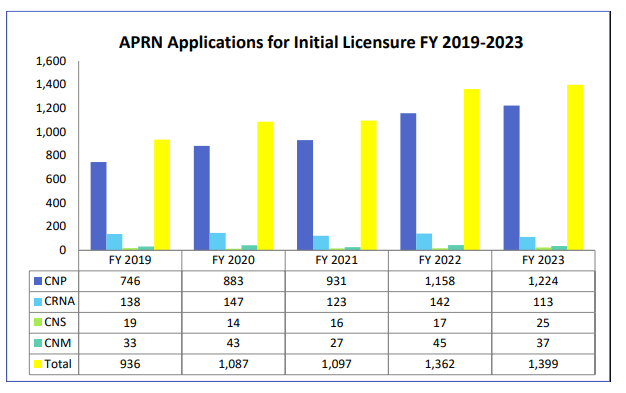
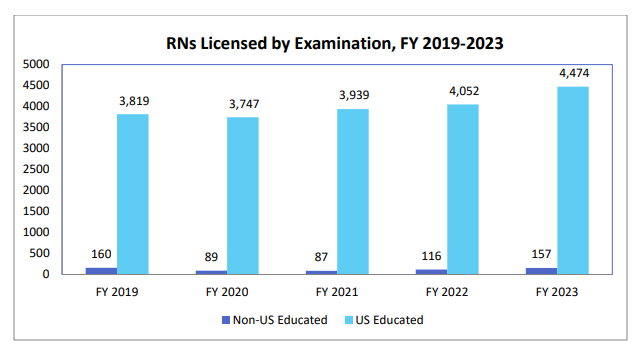
As of mid-2023, Minnesota had 11,919 licensed APRNs. Applicants seeking APRN licensing must submit a detailed application, pay a fee, and satisfy many important requirements. This includes:
- holding an active RN license in Minnesota,
- completion of a graduate-level APRN program accredited by a recognized body,
- current certification in an appropriate APRN role and population focus.
This rigorous process ensures APRNs possess the advanced knowledge and skills necessary to deliver superior patient care.
The following national nurse certification organizations are acceptable as certifying by the MN Board of Nursing:
- American Academy of Nurse Practitioners
- American Association of Critical-Care Nurses Certification Corporation
- American Nurses Credentialing Center
- American Midwifery Certification Board
- National Board of Certification and Recertification for Nurse Anesthetists
- National Certification Corporation for the Obstetric, Gynecological, and Neonatal Nursing Specialties
- Pediatric Nursing Certification Board
Postgraduate practice
Since July 1, 2014, new CNPs and CNSs in Minnesota are required to complete a minimum of 2,080 hours of practical experience. This must be done within a collaborative management setting, typically found in hospitals or integrated clinical environments where APRNs collaborate closely with physicians. This framework is designed to foster a comprehensive approach to patient care, ensuring a mutually agreed plan between the CNP or CNS and one or more licensed Minnesota physicians or APRNs, defining the extent of collaboration needed.
Note, that APRNs registered before July 1, 2014, must submit an affidavit verifying they have completed these required hours, solidifying their commitment to maintaining high standards of care.
Licensure by reciprocity
Minnesota extends a warm welcome to nurses licensed in border states through reciprocity, allowing them to practice within its borders provided certain criteria are met:
- The licensure standards of the border state align closely with those of Minnesota.
- There has been no adverse action taken against the nurse’s license by the border state.
- The nurse is not currently engaged in any alternative or diversion programs.
- There has been no prior denial of a license by Minnesota.
Nurses practicing under this privilege are expected to notify the board within ten days of commencing employment in Minnesota, adhering to the same professional obligations as Minnesota-licensed nurses.
Education waived
In recognition of the valuable practical experience, Minnesota waives additional educational requirements for LPNs licensed in another state who have passed a licensing examination recognized by the board and possess 24 months of LPN experience within the five years preceding the application.
Minnesota Nursing Board Licensure Exemptions
The Nurse Practice Act outlines nine specific scenarios where a Minnesota nursing license is not mandatory, ensuring flexibility and responsiveness to various situations:
- Providing immediate nursing assistance in emergency scenarios.
- Nurses employed by the U.S. government who hold valid licenses from other states.
- Professionals performing within the scope of another licensed occupation or profession.
- Nursing assistants performing delegated functions under RN or LPN supervision.
- Individuals providing care in settings prioritizing spiritual over medical treatment.
- Nurses practicing in Minnesota as part of their formal nursing education from another state.
- Engaging in practice as a student preparing for APRN, RN, or LPN licensure.
- Licensed nurses from other jurisdictions temporarily in Minnesota for educational purposes, such as continuing education or guest lecturing.
State Board of Nursing Minnesota Application Process
Registered Nurses (RNs) and Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs) who have previously been licensed by examination in another state and want to transfer their important abilities to Minnesota can practice through endorsement. Here’s a step-by-step approach to getting through this process:
- Application Submission: Apply online using the Minnesota Board of Nursing Login portal or download the Licensure by Endorsement Application form from the Board’s website. For paper applications, complete, sign, and mail the form along with the appropriate cost.
- Verification of licensing: In addition to getting Minnesota State Board of Nursing license verification, you must also request verification of your initial licensing from the state where you were initially licensed.
- Confirmation of Nursing Employment: If you are presently engaged in nursing, your employer should fill out and submit the Confirmation of Nursing Employment form. If you are not presently employed, please complete this form through your previous or most current nursing employer.
- Criminal Background Check: After applying, you will obtain a fingerprint package from the Criminal Background Check office. Follow the enclosed instructions carefully. For questions, contact [email protected] or call 651-201-2822.
- Continuing Education or Refresher Course: Depending on your nursing activities, you may need to record continuing education credits or complete a refresher course. The Board will advise on this after reviewing your employment confirmation form.
- Monitoring Your Application: Ensure all forms and fees have been successfully submitted and regularly check the status of your application via your online services account.
During this procedure, you may obtain a temporary permission that allows you to continue practicing in Minnesota while the application is processed. This permission lasts for 60 days, or until the license is obtained.
Minnesota Board of Nursing Application by Endorsement Forms
- Endorsement Application Packet for LPN Licensure
- Endorsement Application Packet for RN Licensure
- Endorsement Confirmation of Nursing Employment form
If you are unsure which form(s) are appropriate for your case, please contact our licensing professionals for assistance.
Minnesota RN and LPN Licensure by Examination Application
For those embarking on their nursing career in Minnesota without prior licensure:
- Submit your application with a $105 fee.
- Conduct a criminal background investigation for a charge of $33.25.
- Provide documentation that you finished an approved nursing program.
- Attend a review course if you graduated more than five years ago or haven’t taken the NCLEX in the last 5 years.
- Enroll with Pearson Vue and take the NCLEX for a separate $200 cost.
International nursing program graduates must also submit a Commission on Graduates of Foreign Nursing Schools (CGFNS) Credentials Evaluation report and, if the program was not taught in English, pass an English proficiency exam.
Requirements for Licensure as an APRN
To practice as an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse in Minnesota:
- Hold or be eligible for a Minnesota RN license.
- If it has been more than a year since your previous criminal background check with the Board, complete it.
- Submit the application plus fee for every APRN position you are interested in applying for.
- Successfully complete a graduate-level APRN course.
- Provide valid certification in your role and population emphasis from a board-approved national certifying authority.
It should be noted that Certified Clinical Nurse Specialists and Certified Nurse Practitioners have to fill out a Post-Graduate Practice Verification form, whereas Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists practicing nonsurgical pain treatment must submit a Verification of CRNA Written Prescribing Agreement form.
Minnesota Board of Nursing Border State License Recognition
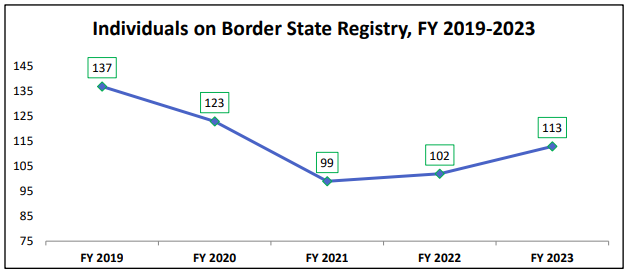
On June 30, 2023, the total number of nurses on the border state registry was 113 (87 RNs and 26 LPNs). Nurses seeking inclusion in the Border State Registry must adhere to specific obligations. Except for meeting the eligibility criteria they must also send a completed Border State License Recognition Report of Employment form along with the required fee to the Board office.
To maintain registration on the Minnesota Board of Nursing Registry, nurses must continuously meet specific criteria. They must submit a new Border State License Recognition Report of Employment form to the Minnesota Board of Nursing within ten days of renewing their border state license. This submission is crucial for registry retention and must be completed before the border state license expiration date.
Nurses are also required to submit a new form within 10 days of ceasing Minnesota employment or starting a new position in the state. Additionally, notifying the Board of any name or address changes is essential.
Note, that upon moving to Minnesota permanently, the nurse becomes ineligible for the registration through border state and must apply for a Minnesota nursing license.
Border State Registry Eligibility
To work as an RN or LPN in Minnesota with no a Minnesota nursing license, the nurse must:
- Have a current nursing license in Iowa, North Dakota, South Dakota, or Wisconsin.
- Reside in the border state where the nurse holds a current license.
- Not have current or past adverse action against the nursing license in the border state.
- Not engage in an alternative or diversion program for medical professionals whose sickness may limit their ability to practice safely, or be recommended by the courts to participate in such a program.
- Not having been denied a Minnesota nursing license or having a current adverse action regarding a Minnesota nursing license that has resulted in the nurse’s removal from practice.
- Work for an organization such as a hospital, clinic, or other healthcare institution or group in Minnesota.
Border State Registry Ineligibility
Nurses employed by temporary agencies or agencies whose primary purpose is other than health care must have a current Minnesota nursing license to practice nursing in Minnesota. Schools, correctional facilities, and manufacturing facilities are examples of employers whose primary function is not to provide healthcare.
A nurse with a current Minnesota license is not eligible for border state recognition until the Minnesota license has expired. Other states’ nursing licenses, including a license labeled “Multistate,” are not valid in Minnesota, except under identified legal circumstances.
Board of Nursing MN Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC)
Minnesota’s bill to join the NLC was introduced in the 2023-2024 legislature, but did not make it out of the Health and Human Services committee.
Understanding Your 2024 Minnesota Nursing License Renewal
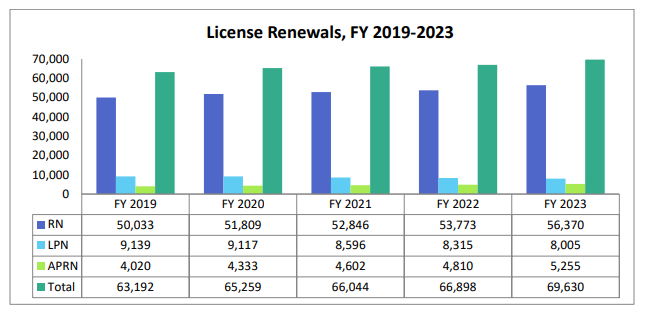
In fiscal year 2023, the Minnesota board of nursing handled 69,630 RN, LPN, and APRN licensure renewal applications. The biennial licensing period is established by the day of licensure in relation to the year and month of the applicant’s birth date. The licensing time might range from 6 to 29 months.
The Minnesota Nursing Board no longer mails paper renewal applications, except you request it by marking the box on the back side of the reminder note and submitting it to the Board’s office. You can also contact the Board to get a hardcopy renewal application.
A reminder postcard is delivered to applicants around three months preceding the expiration of the license. A Minnesota Board of Nursing license renewal reminder email will be sent as well.
Board of Nursing MN Continuing Education (CEU) Requirements
LPNs have to earn 12 contact hours of CE within 24 months after licensure. This is a proportion of one contact hour every two months of enrollment. If your registration duration is less than or greater than 24 months, use the same ratio.
RNs are required to complete 24 contact hours. The ratio of one contact hour per month applies whatever the length of the licensing period.
There are no extra continuing education requirements for APRN license renewal. The certifying organization determines the continuing education requirements for renewing APRN certification.
Preserve the documentation for two years after completing the continuing education.
Minnesota Nursing Board Complaints & Disciplinary Actions
When the board determines that reasons for disciplinary measures arise, it can take any of the following actions:
- deny, revoke or suspend the license;
- impose practice limitations;
- fine up to $10,000 for each violation
- order unremunerated service;
- censure or reprimand the nurse.
A nursing license can be immediately terminated if a court appoints a guardian for a nurse, the nurse is committed, or the nurse is judged to be mentally ill, chemically dependent, or a threat to the public.
The Minnesota Board of Nursing may also temporarily suspend a nurse’s license without a hearing if it determines that there is reasonable grounds to suspect the nurse violated a statute or regulation.
A revoked, suspended, or limited license may be reinstated at the board’s discretion after payment of the expenses of the procedures and the current registration fee.
MN Nursing Board License Verification & Lookup
Minnesota Board of Nursing license verification includes several steps. Access the Board of Nursing website. Navigate to “Online Services” under “Licensees” on the website. All users need to register to create a new online account unless they’ve registered after May 8, 2017.
Click on “Register to Access Site,” choose “Applicant,” and follow the prompts to create a password and complete the New Account Detail. After clicking “Finish,” enter your username and password to log in. The screen will display tabs indicating current open applications and your profile view.
Choose the application you want to review, and check the bottom of the page for an open items checklist. If options are available, a button may appear at the bottom.
Minnesota Board of Nursing license lookup of Advanced Practice Registered Nurse, Registered Nurse, Licensed Practical Nurse Licenses, and Temporary Permits can be accessed through the Online Verification page.
Minnesota Board of Nursing Useful Online Resources
- Minnesota Nurse Aide Registry Search
- MN Health Board Credential Search
- MN Health Board Login
- Minnesota Board of Nursing Licensure
- Board of Nursing Rules
- Minnesota Board of Nursing Nurse Practice Act
- Minnesota Board of Nursing Related Laws for Nurses
- Road Map to Controlled Substance Diversion Prevention
- Minnesota Board of Nursing Reports
- About the Minnesota Board of Nursing
FAQs About The Minnesota Board of Nursing
-
What is the Minnesota Board of Nursing?
The Minnesota Board of Nursing is an oversight organization appointed by the governor that consists of 16 members. It protects public health by governing the education of nurses, licensure, and practice. The Board guarantees that nurses have certain credentials and follow ethical norms, promoting the greatest quality of medical treatment and security in the state. -
Who is on the Minnesota Board of Nursing?
The Minnesota Board of Nursing is made up of 16 members, eight of whom are registered nurses with at least five years’ recent nursing experience. Four registered nurses must have at least five years of clinical or administrative experience. The remaining eight members are four LPNs with at least five years of experience and four public members. -
What are the responsibilities and role of the Minnesota Board of Nursing?
The Minnesota Board of Nursing protects public health and safety by overseeing nursing education, licensing, and practice. It does this through approved activities in accordance with Minnesota legislation and standards, such as nursing knowledge development, public policy advocacy, collaborative alliance construction, information dissemination, and efficient operations. -
What are the services and information provided by the Minnesota Board of Nursing?
The Minnesota Board of Nursing provides a variety of services, such as licensure, discipline control, and program approval. It offers useful information about the training of nurses, practice, and licensure. The Board is dedicated to advancing information relevant to the demands of the general population and nurses, influencing efficient public policy, and preserving transparent interactions with stakeholders. -
How to contact the Minnesota Board of Nursing?
The Minnesota Nursing Board phone number is 612-317-3000. You can send emails to [email protected], and if you prefer to visit the board, you can locate it at 1210 Northland Drive Suite 120, Mendota Heights, MN 55120. The MN Nursing Board’s website is https://mn.gov/boards/nursing/. -
How can I renew my license? Can I mail in a paper renewal application?
The Minnesota Board of Nursing makes it easy to renew your license online. The Board recommends online renewal for a more simplified and effective approach. However, if required, paper forms can be mailed. -
What do nurses need to have ready when starting their renewal online with the Minnesota Board of Nursing?
Nurses should have the following items available before beginning their license renewal online: personal identity information, fee payment details, evidence of continuing education or mandatory training, if applicable, and any extra paperwork asked by the Board. Nurses who have these facts prepared can make the online renewal procedure with the Minnesota Board of Nursing more efficient and timely.



